| ||||
 | ||||
 | ||||
 | ||||
 | ||||
 | ||||
 | ||||
* TECHNOLOGY
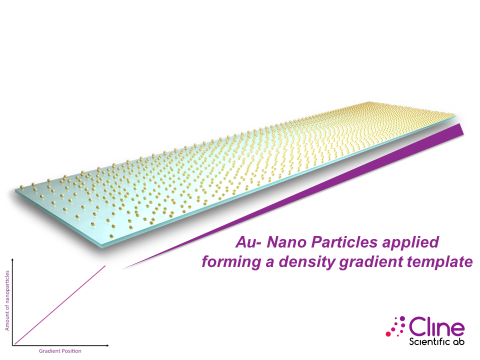
Cline's patented method, used to control the average distance between nano particles, is the key technology in creating a continuous density gradient.
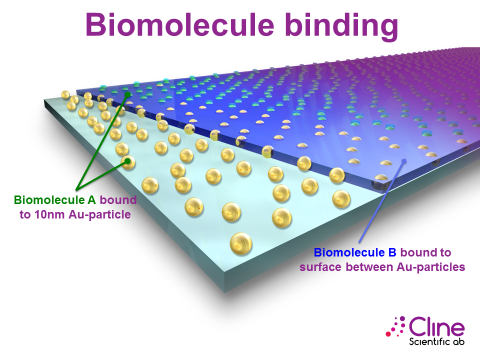
There are two sites where your biomolecule of choice can bind to the Cline Nano Gradient:
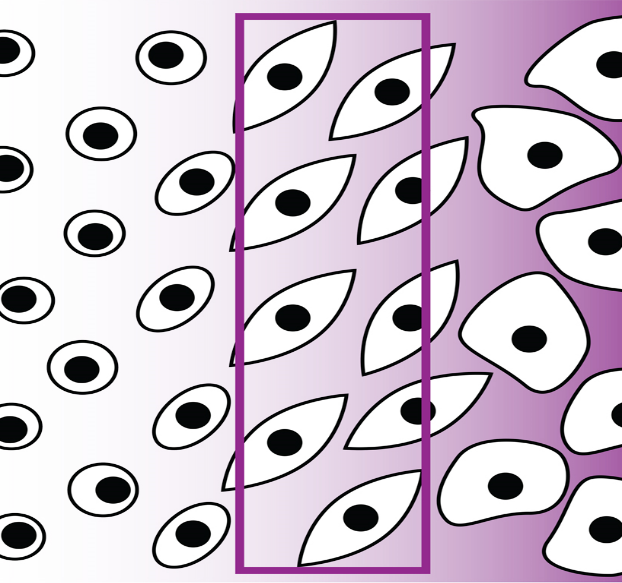
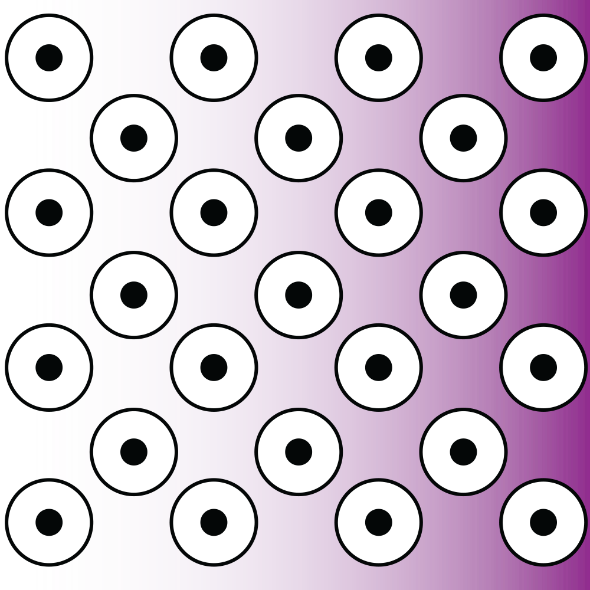
- The first location to bind molecules is the nanoparticle gradient itself (Biomolecule A in figures 1 & 2).
- The second binding-site is the surface space between the nanoparticles (Biomolecule B in figures 1 & 2).
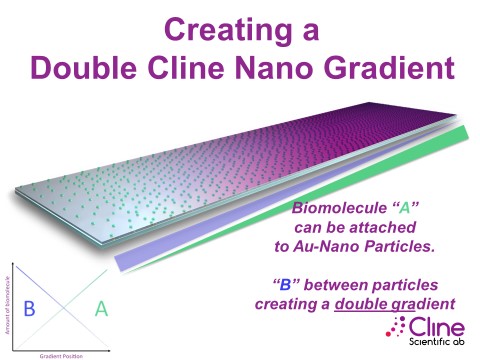
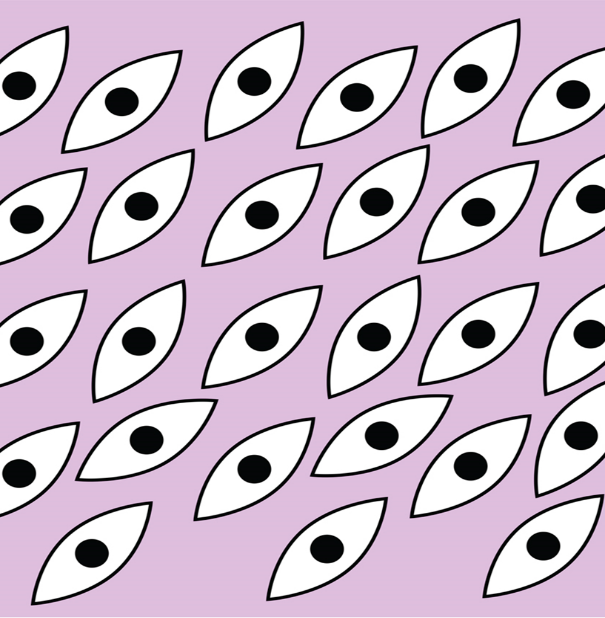
When both sites are coupled with biomolecules, it forms a double gradient, as shown in figure 2.
Pioneer and world leader in providing Gradient Surfaces based on nanotechnology
Product Basics
Cline Scientific is the only company in the world providing surface gradients of nanoparticle-bound molecules for in-vitro applications. Cline Nano Gradients and Cline Nano Surfaces consist of nano-patterns of gold nanoparticles onto which biomolecules can be attached to create surfaces mimicking tissue function at the molecular level.
The unique feature of the Cline Nano Gradient is the continuous dispersion of the gold nanoparticles onto a surface in a gradient pattern. This gradient can be utilized to screen for sensitive reactions/interactions between cells and molecules, thus determining the optimal composition of biomolecules responsible for a certain cellular response. The region on the gradient responsible for a reaction can be recreated in a Cline Nano Surface.
* BIOMOLECULE BINDING
Figure 1 Binding Sites
Figure 2 Double Gradient
Binding method (examples)
**Nanoparticles are positively charged, which allows for electrostatic coupling.
Biomolecule A Biomolecule B
Biomolecule B
Thiol-linker-A Electrostatic Binding*
Electrostatic Binding*
Thiol-PEG-Neutravidin<->Biotin-A
Thiol-Neutravidin<->Biotin-A
Applications:
1. STEM CELL DIFFERENTIATION
“One surface replaces thousands of experiments”
1. Seed cells
Seed your cells on a Cline Nano Gradient of surface- bound molecules.
2. Analyze and select
Allow the cells to react to their surroundings and then identify your optimal surface composition.
3. Reproduce
The Cline Nano Surface recreates the optimal conditions for your cells and allows you to reproduce your results.
Benefits
• Safely select homogenous cell populations
Safely select homogenous cell populations
• Screen for cell responses using a gradient
• More experiments done in less time
More experiments done in less time
• Mimic tissue function
Mimic tissue function
The immediate environment is critical for stem cells in regulation of their function. The use of Cline Nano Gradient to screen for the exact needs of your cells, allows for faster advances in stem cell R&D. The area in the gradient where optimal cell differentiation is found can then easily be recreated using Cline Nano Surface.
Application Notes
2. CANCER RESEARCH & CELL MIGRATION
“One surface replaces thousands of experiments”“Ultimate cell control through molecular precision”
1. Seed cells
Seed your cells on a Cline Nano Gradient of surface bound biomolecules.
2. Migration
Study how the cells migrate on the surface gradient of biomolecules.
3. End point
Quantify cell migration according to your preferred method (e.g. cell numbers, motility, viability, or distance migrated)
Benefits
• Study directional cell migration
Study directional cell migration
• Specific migration along a continuous surface gradient
• Cell control at the molecular level
Cell control at the molecular level
• Screen for change in cancer cells’ migratory behavior
Screen for change in cancer cells’ migratory behavior
The Cline Nano Gradient can be utilized to study sensitive gradual cell behaviors such as cellular movement and cell migration. This is achieved by creating a surface gradient of biomolecules stimulating cellular movement. Cells are cultured, then analyzed by live imaging or by staining.
Iwai North America Inc.
541 Taylor Way Suite# 4
San Carlos, CA 94070
Phone : (650) 486-1541
Fax : (650) 394-8638
Open weekdays 9 AM-6 PM (PST)
.........................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
.....................................................
.....................................................
 | ||||